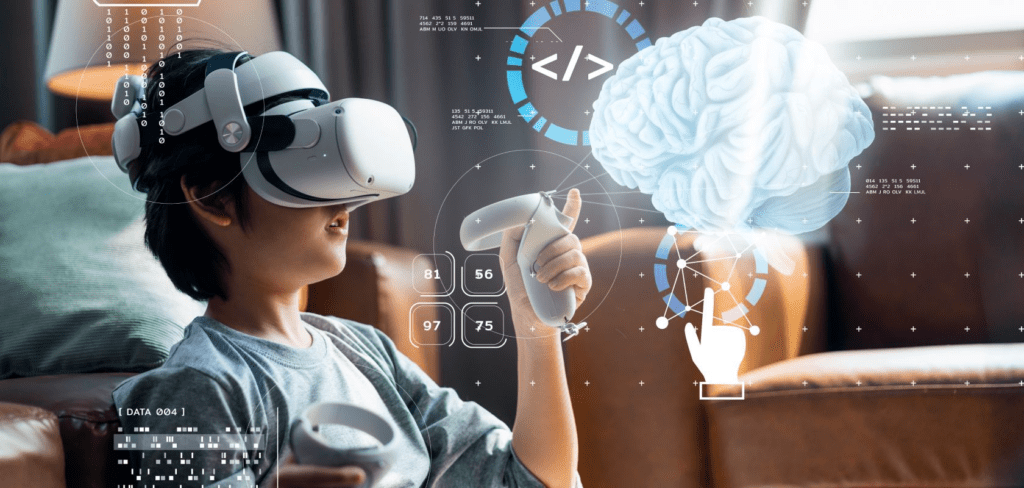
Technology is now a revolutionary force in education, improving student learning and changing conventional teaching approaches. The use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in the classroom is one of the most inventive trends in this field. This essay explores the applications, advantages, and changing landscape of immersive learning as it digs into the significant effects of AR and VR technology on modern education.
Immersion technologies such as augmented reality and virtual reality overlay or build a simulated world to give users richer experiences. Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that augments the physical world with digital content, typically accessed via gadgets like smartphones or AR glasses. Conversely, virtual reality (VR) submerges viewers in a wholly synthetic setting, usually accessed via VR headsets.
Uses in the Field of Education:
1. Dynamic and interactive learning modules:
covering a wide range of subjects are provided via AR and VR. For example, using augmented reality (AR) applications, biology students can investigate 3D models of the human body, dissecting virtual organs and learning more about anatomical features.
2. Virtual Field Trips:
Logistical obstacles are no longer a barrier to traditional field trips. Through virtual field trips made possible by AR and VR, students can visit historical sites, natural environments, or even space. This immersive method creates a first-hand virtual experience that improves comprehension and engagement.
3. Language Learning:
Immersion technologies have a major positive impact on language acquisition. Augmented reality applications facilitate vocabulary acquisition by superimposing translated words onto real-world items. By immersing language learners in simulated settings where they can practice conversing with virtual characters, virtual reality aids language learners.
4. Science experiments :
can be conducted in a safe and regulated virtual environment by students using VR simulations to bring laboratories into the classroom. This is especially helpful for schools who are working with risky experiments or have limited resources.
5. Historical Reconstructions:
With AR and VR, historical events can be reenacted, bringing history to life. Pupils can experience significant historical events, digitally explore ancient civilizations, and have a greater understanding of the background to historical narratives.
AR and VR’s advantages in education
Enhanced Engagement: Students are drawn in and encouraged to participate actively because AR and VR are immersive technologies. Comprehending complex topics becomes easier when they are approached as an experiential journey.
1. Multi-Sensory Learning:
By appealing to a variety of senses, AR and VR offer a comprehensive educational experience. This multimodal method improves comprehension and memory retention.
2. Adaptability to Varying Learning Styles:
AR and VR are capable of accommodating the various learning styles that students possess. Kinesthetic learners can participate in interactive virtual activities, while visual learners can gain from 3D visualizations.
3. Global Connectivity:
Students from all over the world are connected through virtual classrooms, which eliminate geographical boundaries. Projects involving collaboration become seamless, promoting cross-cultural dialogue and an international viewpoint.
4. Safe and Controlled Environments:
Virtual reality simulations offer a risk-free environment for scenarios or experiments that could be dangerous or difficult in a conventional classroom. This guarantees that students are free to experiment and learn without worrying about the real world.
Obstacles and Things to Think About:
Despite the fact that AR and VR have many benefits for education, there are drawbacks. Notable factors include the cost of implementation, the accessibility of technology, and the requirement for educators to receive specialized training. It also takes careful planning to make sure that these technologies complement curriculum and educational goals.
1. Cost Implications:
Purchasing hardware, software, and training are necessary for integrating AR and VR in the classroom. Cost is still a problem, particularly for educational institutions with little funding.
2. Technical Infrastructure:
Robust technical infrastructure is necessary for a smooth AR and VR experience. Schools require compatible devices and dependable internet access, which can be difficult in some areas or communities.
3. Content Development:
Specialized skills are required to create high-quality educational content for AR and VR. In order to create engaging and productive learning environments, educators and content creators require training.
4. Health and Safety Concerns:
Using virtual reality headsets for extended periods of time can cause some users to feel uncomfortable or sick. Teachers must take into account the health and safety of their students, particularly those in younger age groups.
5. Curriculum Integration:
AR and VR should improve and supplement current curricula. Careful planning and alignment with learning objectives are necessary for the seamless integration of these technologies into educational frameworks.
Immersive Learning’s Future:
The future of immersive learning is being shaped by the constant advancements in augmented reality and virtual reality. Technology has the potential to be widely adopted as it becomes more affordable and accessible. New innovations like Mixed Reality (MR), which combines aspects of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality, increase the potential for dynamic and captivating learning environments.
1. Personalized Learning Paths:
As AR and VR technologies advance, so does the possibility of creating more customized learning routes. These tools enable customized learning experiences by responding to each person’s growth and preferences.
2. Collaborative Learning Spaces:
By using virtual reality (VR), educators can create shared virtual environments in which students from various locations can engage with one another. This encourages cooperation, group dynamics, and the sharing of ideas across geographical boundaries.
3. Professional Development for Teachers:
Teachers must continue their professional development as a result of integrating AR and VR. Teachers can fully utilize the potential of these technologies in the classroom with the support of training programs.
4. Increased Programs for Career Readiness:
Virtual reality (VR) can transform career readiness initiatives by providing realism-based simulations and online internships. Before entering the workforce, students can acquire useful skills and insights into a variety of professions.
5. Constant Innovation in Education:
As AR and VR applications continue to advance, teaching methods will also continue to change. These technologies promise an ever-expanding array of possibilities for enhancing the educational experience, from historical reenactments to virtual science labs.
Virtual and augmented reality are essential elements of contemporary education, not merely sci-fi ideas. It is indisputable that these technologies have a revolutionary effect on how students learn and interact with content. AR and VR have the potential to completely transform conventional teaching strategies and build a more diverse and engaging learning environment through simulated experiments and virtual field trips. Immersion learning is starting to materialize from the virtual as we negotiate the changing interface between technology and education.